Robot Manipulation
Implementing Cartesian Control and Numerical Inverse Kinematics for UR5 and a KUKA iiwa Manipulators in RViz
- The Interactive Marker on the end-effector has two modes: Cartesian Control Mode and Inverse Kinematics Mode.
- Whenever a command is received on the “/cartesian_command” topic, the code computes appropriate joint velocities in response, and then publish them on the “/joint_velocities” topic once for every time a command is received.
- Whenever a command is received on the “/ik_command” topic, the code computes appropriate joint positions in response and publishes them on the “/joint_command” topic.
Implementing Collision Free Motion Planning Algorithm for KUKA iiwa and UR5 Manipulators
- The start point of motion planning using the Randomly Exploring Random Trees is a goal expressed in joint space. The goal is received is in end-effector space and the code performs collision free Inverse Kinematics using MoveIt! framework on it to obtain a goal configuration in joint space.
- The Randomly Exploring Random Trees algorithm is implemented to find a collision free trajectory for different obstacles and publish an appropriate joint trajectory between the start and end point, by sampling joint values within the joint ranges
Machine Learning
Predicting Vehicle Economy using Linear, Polynomial and Ridge Regression
- Implementing Linear Regression, Polynomial Regression and Ridge Regression from scratch to predict Vehicle Economy using vehicle attributes such as horsepower, number of cylinders, engine displacement, weight, acceleration and make year


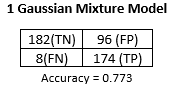
Predicting Spam v/s Not Spam Emails using Expected Maximization Algorithm for GMM
- Implementing the Expected Maximization Algorithm for a 1, 2, 3, and 4 Gausian Mixture Model from scratch and using it as a Bayes Classifier for identifying spam emails
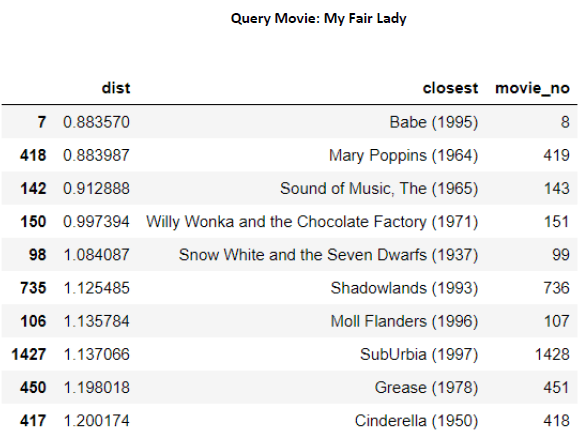
Movie Recommendation System using Collaborative Filtering
- Implementing Collaborative Filtering using the Matrix Factorization MAP inference algorithm from scratch on the Movie Lens Dataset collected by the Group Lens Research Project at the University of Minnesota.
- The dataset consists of 100,000 ratings (1-5) from 943 users on 1682 movies. 10 most Similar movies have been identified by using the Euclidean distance on the embedded representation of the movie.
- Dataset Link: movielens.umn.edu
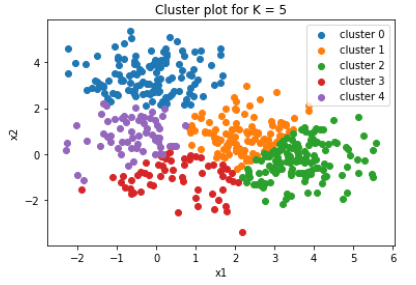
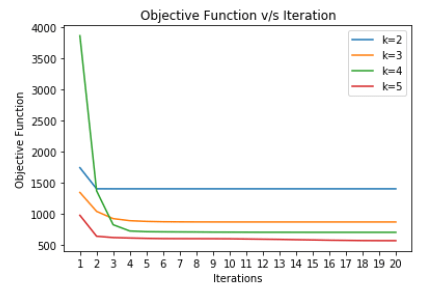
K – Means Algorithm
- Implemented the K – Means algorithm from scratch, on a data-set with 500 data-points generated from a mixture of 3 different Gaussian distributions
- Visualized the change in objective value function with each iteration, for different cluster values
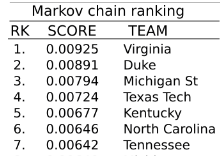
Predicting CFB 2019 Rankings Markov Chains
- Modeling the match scores of 769 college football teams based on the scores of CFB 2019 season as a Markov Chain to predict the team rankings at the end of season.
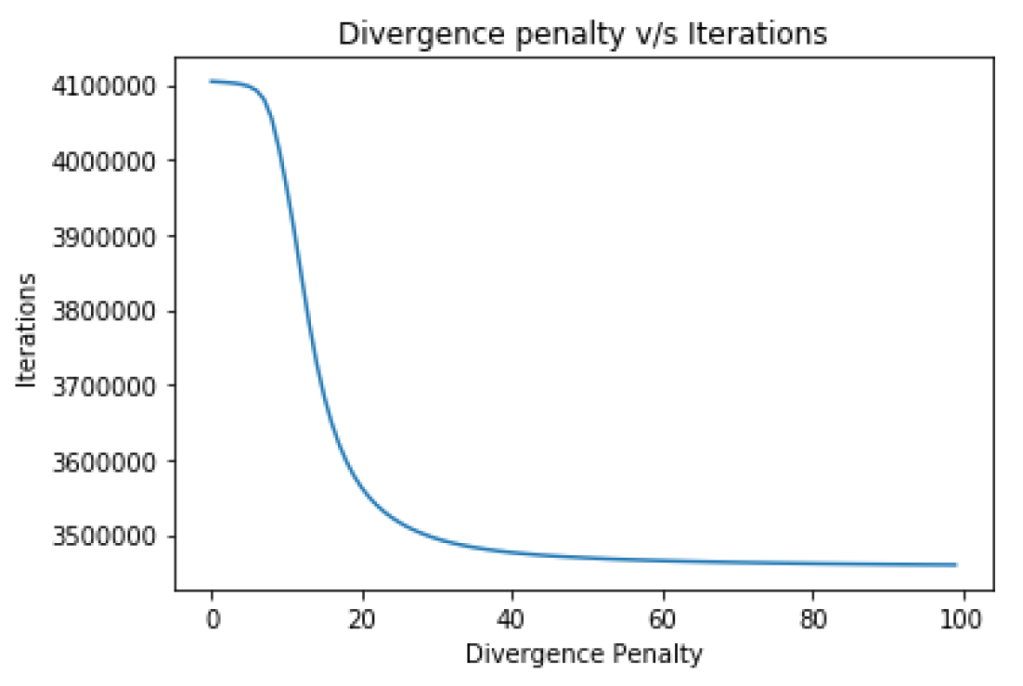
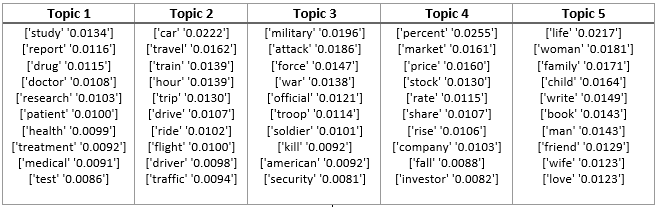
Topic Modeling for New York Times articles using Non Negative Matrix Factorization
- Learnt 25 topics by implementing the NMF algorithm with Divergence Penalty from scratch, for 8447 documents from the New York Times. The vocabulary size is 3012 words.
- Identified 10 words with the largest weight for each of these 25 topics, thus representing a summary of the topic learnt using this algorithm.
Robot Learning
Estimating Mobile Robot State using Extended Kalman Filter
- Estimating 2D robot pose using sensor data consisting of a range and bearing for landmarks the robot can see and implementing a dynamic model and EKF for publishing translational and angular velocities used to perform localization
Behavioral Cloning using Classical Machine Learning for Robot Navigation
- The goal of this projects was to learn an appropriate behavior for the agent by imitating demonstrations from an expert user. These demonstrations have been collected by a human controlling the agent via a keyboard.
- The code uses RGB image observations in this environment, with the groundtruth location of the agent in each image, expressed in the maze coordinate system. as training data. After pre-processing and dimensionality reduction, the data is used to train Support Vector Machines and Logistic Regression Classifiers
- In the video below, the agent is shown by a green dot and the goal is shown by a red dot
Behavioral Cloning using Deep Learning for Robot Navigation
- Training a DNN and CNN Policy with cross entropy loss using PyTorch on demonstrations from an expert user to learn how to reason about what an obstacle is, and how to go around it, based on obstacle maps which are RGB Image observations of the maze setting
- In the video below, the agent is shown by a green dot and the goal is shown by a red dot
Using Reinforcement Learning for Robot Navigation
- In this project, the agent is allowed to explore the environment by itself and learn from reward signals using a Deep Q Network
- The “robot” (also called “agent”) is shown by the green dot. The goal location is shown by the red square. The agent is required to navigate to the goal. Also, the action space now contains all four directions: ‘up’, ‘down’, ‘left’ and ‘right’ in 3 obstacle maps as shown below

Applied Machine Learning
Classifying Infected Cells with Malaria and Uninfected Cells
- Implementing a CNN to classify cells infected with malaria against those that are not. and improved the performance of the baseline model using data augmentation and mirroring
- Used existing architectures to build a network and training weights from scratch, as well as using pre-trained weights using the ResNet50 architecture from Keras and compared their performance
- Dataset Link: https://lhncbc.nlm.nih.gov/publication/pub9932
Predicting Used Cars Prices
- The data was preprocessed which involved removing all the outliers from features like price, odometer, year and using one hot encoding, target encoding on categorical values. Polynomial Feature Expansion was also used
- Implemented a variety of Linear models such as Linear, Lasso and Ridge Regression and tree based models such as Gradient Boosting and XG Boost to predict the vehicle price using more than 50 feature
- Feature Selection was done using Recursive Feature Selection and Model based selection to visualize feature importance, and a new XG Boost model was modeled on these features, which returns a better score
- Dataset Link: https://www.kaggle.com/austinreese/craigslist-carstrucks-data

Predicting Wine Ratings based on consumer reviews
- Used Bag of Words approach on the consumer reviews for different varieties of wine and combined it with non text features to build a prediction model and tuned the model using tf-idf rescaling and n-grams.
- Dataset Link: https://www.kaggle.com/zynicide/wine-reviews
Artificial Intelligence
2048 Solver
- Modeled the 2048 game as an Adversarial Search problem and implemented the Expecti-minimax algorithm with Alpha Beta Pruning
- Heuristics such as monotonicity, smoothness, and maximum value on the board to achieve a success rate of over 70% in achieving 2048 on the board
- The video below shows the solver playing the game, where the computer spawns the number 2 or number 4 tile randomly, in the output window
Sudoku Solver
- Implemented a Sudoku Solver using backtracking search and the minimum remaining value heuristic, and applied forward checking to minimize the variable domain
- Below are a few statistics for the solver, when used to solve 400 boards
No of boards solved from sudokus_start.txt: 400
Average time taken to solve a board (in seconds): 0.17466574847698213
Standard deviation time taken to solve a board (in seconds): 0.24058147020653406
Minimum time taken to solve a board (in seconds): 0.01299285888671875
Maximum time taken to solve a board (in seconds): 2.0585010051727295
9 Puzzle Solver
- Implemented BFS, DFS and A* search algorithms to build the 9 Puzzle Solver
Self Driving Cars
Self Driving Vehicle Control
- Implemented PID Longitudinal Control for throttle output and Pure Pursuit Lateral Controller for steering angle output to control the vehicle to follow a race track in the Carla simulator
- The speed, throttle input and steering angle of the car are plotted on the fly, as the vehicle moves around the racetrack in the video shown below